Many observability teams use Redis, an in-memory data store, to optimize their telemetry data at scale. Redis offers fast lookups and supports a variety of data structures, enabling cache and retrieval workflows that allow teams to perform contextual enrichment, volume reduction, and anomaly detection. However, wiring Redis calls into workflows with brittle scripts or custom tooling can be inefficient without the proper connection logic — and can even be unsafe if encryption isn’t handled properly.
With Edge Delta’s Telemetry Pipelines, teams can securely connect to their Redis infrastructure, extract key context, and use it to enrich telemetry data pre-index before sending it to downstream platforms for monitoring and analysis. Additionally, Edge Delta’s custom “EDXRedis” OTTL extension reduces management complexity by handling connection pooling, retry logic, and encryption under the hood, empowering users to run any Redis command across any deployment mode by configuring simple OTTL expressions.
Automate workflows across SRE, DevOps, and Security
Edge Delta's AI Teammates is the only platform where telemetry data, observability, and AI form a self-improving iterative loop. It only takes a few minutes to get started.
Learn MoreIn this post, we’ll walk through how to configure Redis-powered processing in an Edge Delta Pipeline, and demonstrate how it improves analysis in any downstream destination, including Edge Delta’s own Observability Platform.
How Does Edge Delta Integrate With Redis?
Edge Delta’s vendor-neutral Telemetry Pipelines can connect with any Redis instance, including Standalone, Cluster, and Sentinel deployments. They work by establishing a secure connection to the specified instance and opening a channel of communication to perform remote read and write operations.
All operations are configured in the pipeline using the EDXRedis function, where teams provide the necessary connection details for their Redis instance, including access URL and authentication credentials. Once the connection is established, teams can build EDXRedis statements to use Redis’ comprehensive command set to perform a wide range of processing operations.
To illustrate, let’s configure an Edge Delta Pipeline to collect synthetic JSON web application data and use Redis to perform two key processing operations: enrichment and deduplication.
First, we’ll follow Edge Delta’s documentation to deploy a new Cloud Pipeline in Edge Delta’s UI, and configure a TelemetryGenerator Node to generate synthetic log data for the pipeline to collect. Then, we’ll add a new Multi-Processor Node to build out our EDXRedis command:
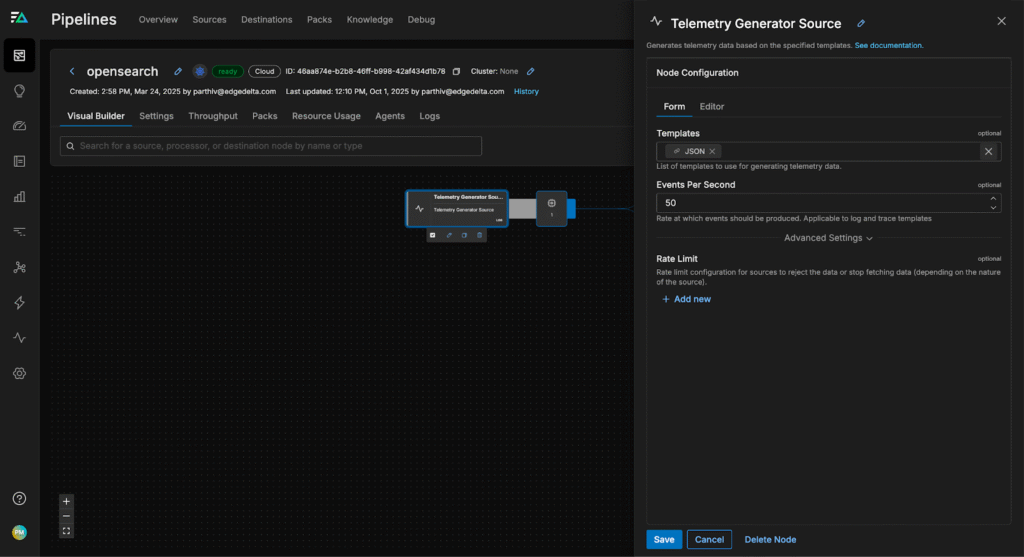
Now, we can establish a connection with our Redis deployment (for this scenario, we’re using a cloud-hosted standalone Redis instance — for detailed information alternate deployments, visit our EDXRedis documentation). We’ll use a Custom OTTL processor to save our connection request, and run a quick “PING” test to verify our connection using the configuration shown below:
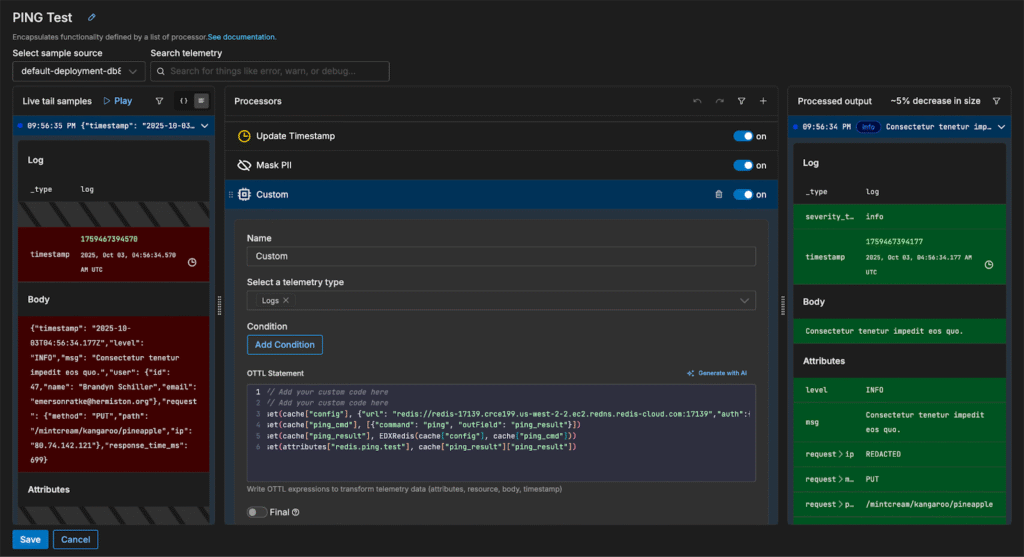
This sends a PING to the Redis instance and stores the response in the log’s redis.ping.test attribute. If successful, we’ll see Redis respond with PONG, confirming the connection. If we check the logs in Edge Delta’s Log Search, we can verify that our Redis connection is up and running:
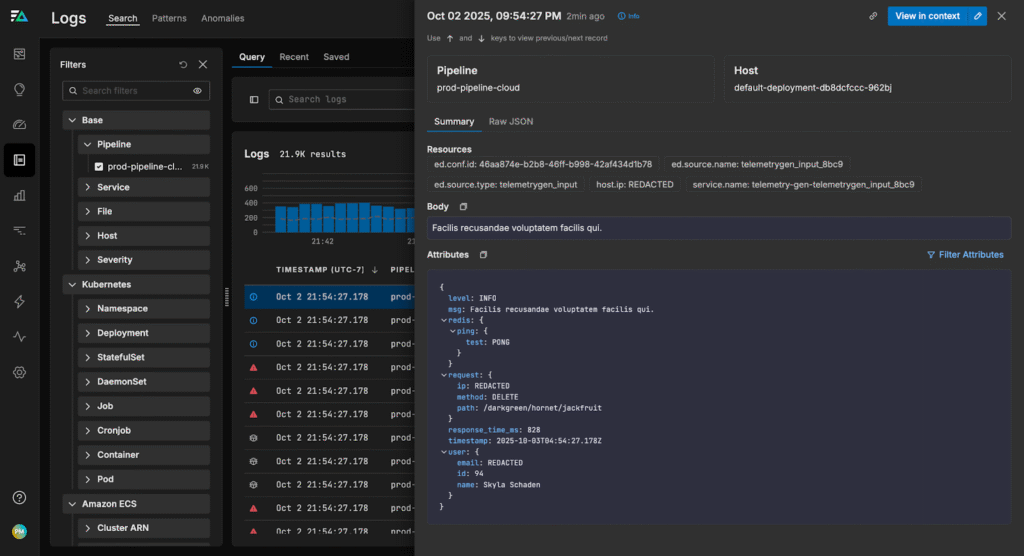
Now that we’re connected, we’re ready to move on to processing.
Redis-Powered Log Enrichment
Our synthetic log data captures information about users accessing specific web pages. To identify potential hotspots or regions with page render issues, we need to correlate each user’s activity with their geographic location. Since this location mapping is stored in our Redis instance, we can create an EDXRedis command to find each user’s respective location, and enrich the logs accordingly.
First, we’ll create a new “GET” command that uses each log’s user id field as the key and queries Redis for the corresponding location value. Then, we’ll save it in the “geo_location” attribute:
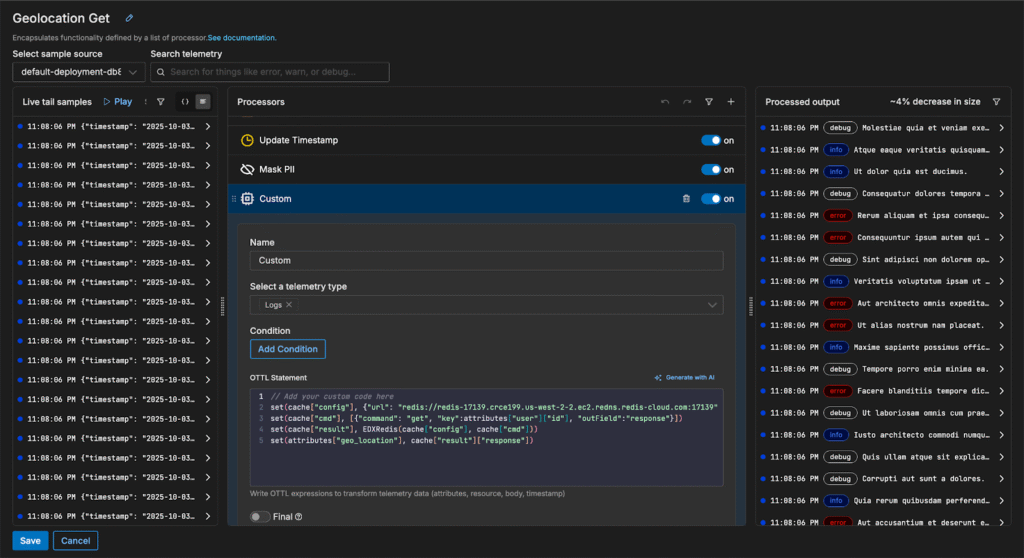
If we navigate to the Log Search page, we can see each log is tagged with geographic information:
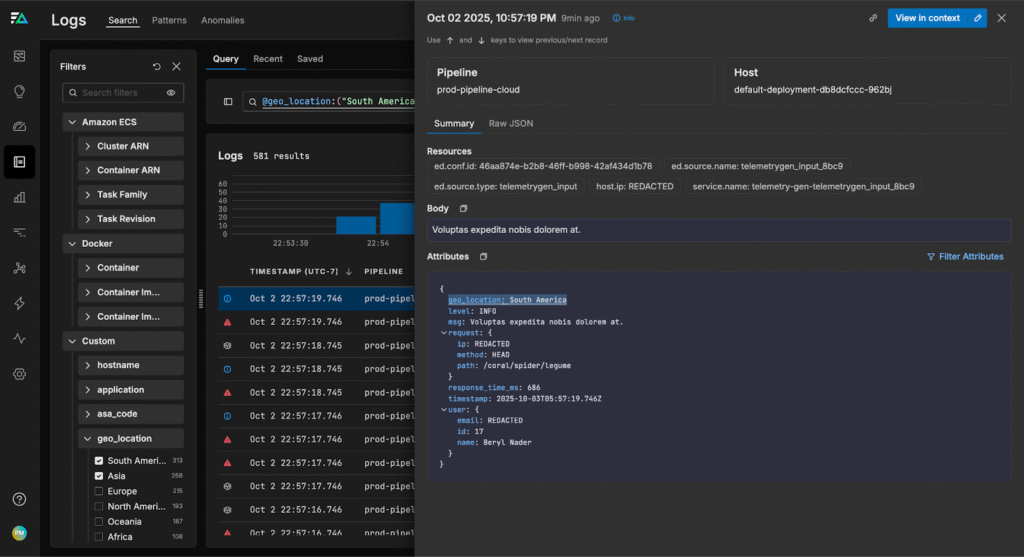
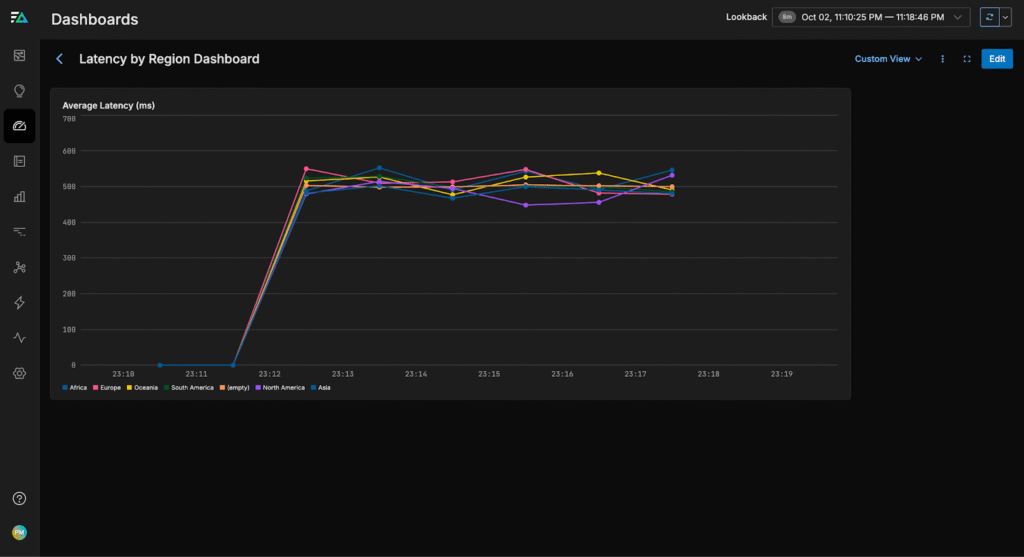
From here, we can build a dashboard to monitor page load latencies by region, helping us quickly identify and troubleshoot issues in any specific area:
Data Deduplication with Redis
If we only care about tracking individual log events to see which actions have occurred, we can use Redis to deduplicate logs and minimize downstream ingestion. By maintaining a cache of logs seen over a set interval, we can check incoming logs against it, tag repeats, and filter them pre-index within the pipeline.
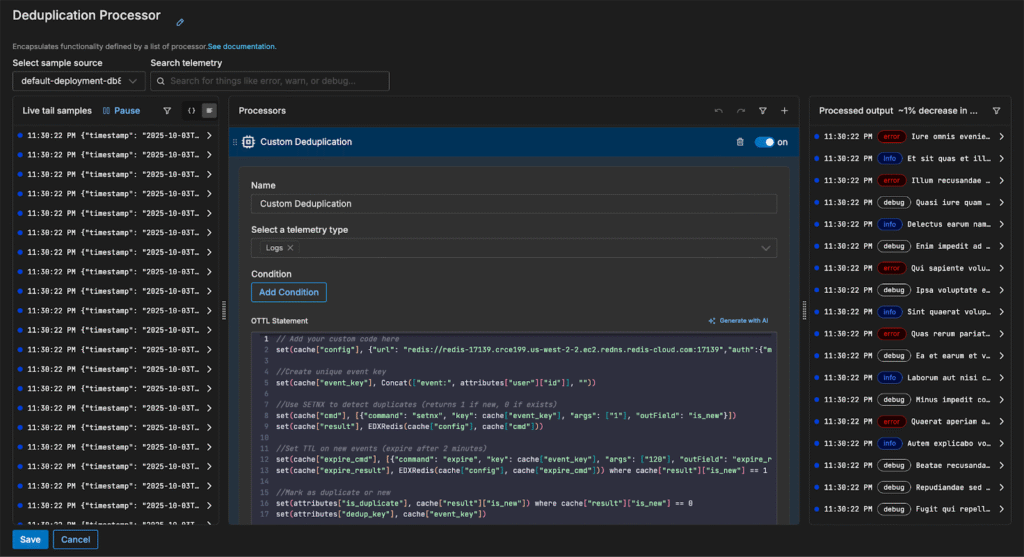
First, we’ll create a unique key for each event using the user’s ID. For example, if a user has an ID of 123, the key becomes “event:123”. This key will be used to track whether we’ve already seen this particular event.
Then, we’ll check if the event is new by using Redis’s SETNX command. SETNX will set the key only if it doesn’t already exist, returning 1 for a new event and 0 if it’s a duplicate.
For events that are new, we set a short expiration time of two minutes. This ensures that Redis only keeps the event key temporarily, allowing deduplication for a limited window without permanently storing all events.
Finally, we create a new “is_duplicate” field that contains “1” if the log is a duplicate event, and “0” if it isn’t.
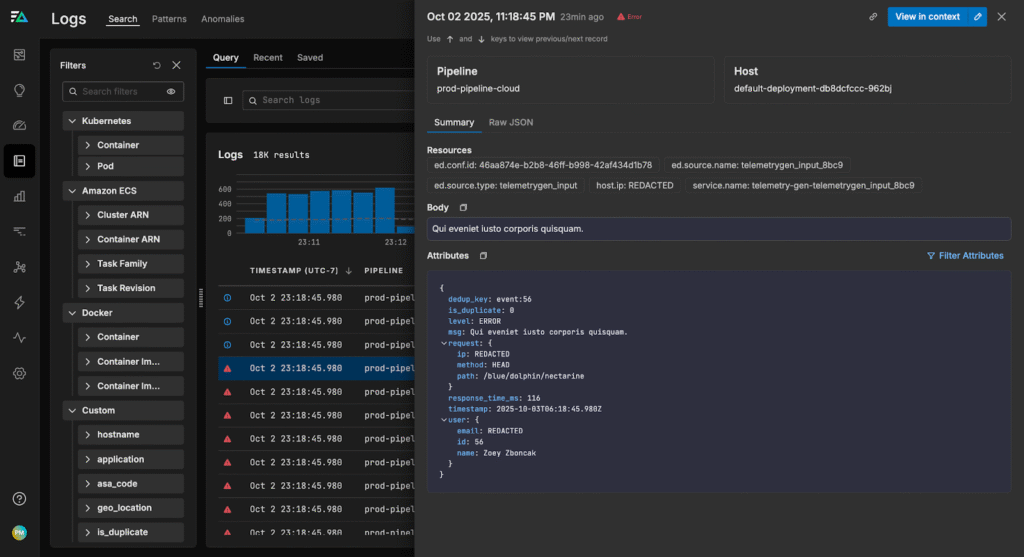
If we check Log Search, we can see the logs are tagged with the new dedup_key and is_duplicate attributes:
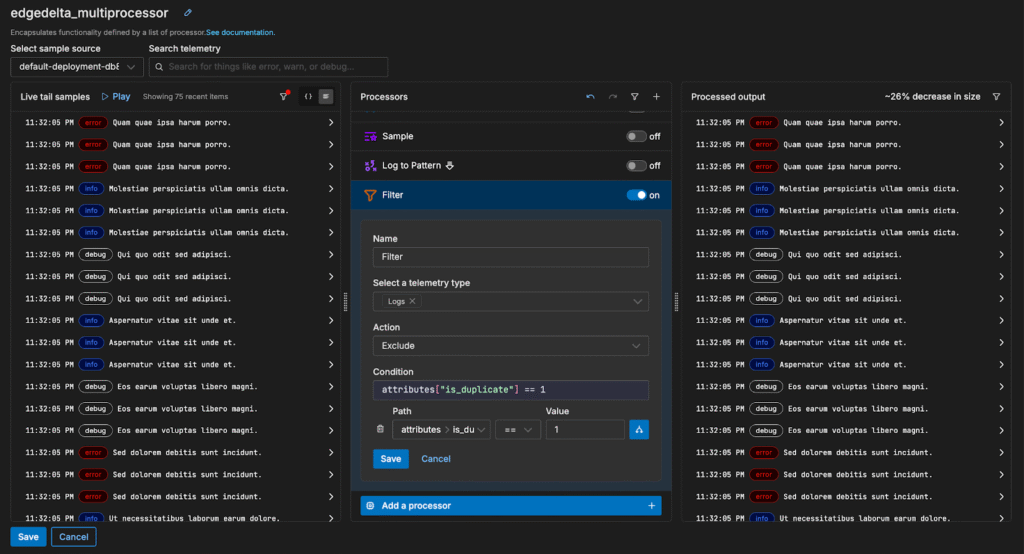
From here, we can filter out repeat logs with a simple check on the “is_duplicate” field — in this case, reducing our log volume by 26% without sacrificing visibility:
By maintaining a cache of known logs in Redis, and accessing it with our pipeline, we can avoid tracking duplicates manually and quickly filter out redundant messages before they overload our downstream analysis platforms.
Conclusion
Redis is a powerful tool that enables a wide range of telemetry processing tasks, including enriching logs with external data, maintaining a cache of recent events to deduplicate logs, and performing other context-based lookups.
Edge Delta’s Telemetry Pipelines simplify Redis integration for teams working at any scale. With our custom EDXRedis function, you can securely connect to your Redis instance, handle encryption, and perform Redis operations — all with just a few simple OTTL statements. This means you can spend less time wiring up infrastructure and more time gaining actionable insights from clean, context-rich telemetry data.
To explore our Telemetry Pipelines for yourself, visit our free, interactive Playground environment or book a demo with a technical expert.