Since IT businesses handle sensitive data, any data leakage, loss, or mismanagement can lead to customer distrust. In the US, 66% of consumers don’t trust businesses that suffered from a data breach. Governments and regulatory bodies impose compliance requirements and standards to avoid these issues. Further, these guidelines ensure that business processes are secure enough to protect customer data.
With 94% of users valuing global data privacy regulations, IT companies must adhere to them to improve reliability and reputation. These requirements and standards protect businesses from unethical or illegal practices, avoiding costly penalties, reputational damage, and other consequences.
Automate workflows across SRE, DevOps, and Security
Edge Delta's AI Teammates is the only platform where telemetry data, observability, and AI form a self-improving iterative loop. It only takes a few minutes to get started.
Learn MoreThis article discusses critical IT compliance standards, including their implementation, challenges, and solutions.
| Key Takeaways • Compliance requirements and standards are guidelines for protecting customer data by ensuring secure business processes. • Since IT firms manage massive amounts of sensitive data, meeting these requirements is crucial to avoid penalties, reputational damage, and more. • The most common compliance requirements and standards include the GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, PCI DSS, GLBA, and FISMA—businesses’ compliance with those ensures legal and operational success. • Compliance requirements involve solving complex regulations, staff lapses, siloed functions, lack of centralization, and AI flaws. • Businesses must train their employees, overcome silo mentality, centralize operations, and hire compliance experts to ensure effective compliance management. |
Understanding Compliance Requirements and Standards
Compliance requirements and standards in IT ensure security, privacy, and ethical data handling among companies. They increase customer and investor confidence, providing an edge over competitors. Moreover, they save companies from the risks of penalties, data loss, and other impacts.
Since only 41% of consumers trust IT companies with their data, meeting regulatory compliance is necessary. The following section discusses the most common compliance requirements and standards every IT company must adhere to.
Common Compliance Requirements and Standards
Since IT firms usually handle sensitive and personal data, they are required to comply with strict privacy regulations. As a consequence, compliance with regulatory requirements in IT is non-negotiable.
| Fun Fact As more users provide sensitive data online, privacy regulations continuously emerge. According to predictions, modern privacy regulations will cover 75% of the world’s population’s data. |
Various regulations apply depending on a business’s size and location. Governments impose some, while independent bodies impose others. Here’s a compliance standards list for IT firms.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR is the European Union’s comprehensive personal data protection and privacy law. It imposes obligations on organizations that target data or offer goods to EU data subjects.
A data subject is a person whose personal data can be collected. GDPR enables them to request access to personal data an organization stores on them and have it updated or removed.
The implication is that all information an organization has about them must be accessible and interrogatable.
GDPR data subjects have the following rights:
- Right to Be Informed
- Right to Access
- Right to Object
- Right to Rectification
- Right to Erasure
- Right to Restrict Processing
- Right to Data Portability
All GDPR requirements are based on seven fundamental principles. If you process personal data, you have to do so according to the following:
GDPR and the Cloud
Under GDPR, cloud service providers entrusted with data must implement robust security protocols. Businesses using cloud services must also ensure data storage, processing, and transfer to comply with regulations.
Organizations can ensure GDPR compliance when using cloud services through the following:
- Selecting cloud providers with compliance tools and certifications
- Regularly auditing and monitoring data stored in the cloud
- Implementing security measures
- Securing access controls
Some known GDPR-compliant storage vendors are Amazon Drive, Google Drive, and Microsoft OneDrive.
Those violating the GDPR privacy and security standards must pay substantial fines. In 2023, the top 5 social networking sites paid GDPR over $3.1 billion. GDPR Penalties can reach up to €20 million or 4% of your annual revenue from the preceding year.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA is a federal law enforced by the US Department of Health and Human Services. It requires national standards for healthcare data management, protecting them from being disclosed without consent.
Any organization or third party that handles or manages protected health information (PHI) must safeguard them. This protection is achievable through reasonable physical, administrative, and technical measures.
HIPAA requires that all PHI be accessed only by authorized parties. Any security breach should be reported and resolved.
To keep protected electronically stored PHI private, HIPAA imposes the following requirements:
| Requirement | Description |
| Privacy Rule | Individual rights to access and review a copy of their PHI and request modifications |
| Security Rule | Safeguards for PHI confidentiality while maintaining its integrity and availability to those authorized |
| Breach Notification Rule | Entities must notify breaches affected individuals, regulating body OCR, and the media (in significant breaches) |
HIPAA and the Cloud
Healthcare organizations turn to the cloud to streamline operations. HIPAA-compliant cloud services let them securely store sensitive patient data and prevent them from losing in data breaches or natural disasters.
In a HIPAA-compliant cloud, the healthcare organization must develop policies and procedures for using HIPAA-secure cloud storage of ePHI, which refers to Electronic Protected Health Information.
Meanwhile, the cloud service provider must meet HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules provisions before handling any ePHI. They must periodically review HIPAA regulations and revise their products, policies, or procedures.
Corrective action plans, potential imprisonment, and fines ranging from $137 to $68,928 are penalties for HIPAA violations.
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act)
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act is a financial compliance standard that requires public companies to ensure the accuracy of financial data. It covers policies on storing, managing, and accessing financial data in the cloud.
This US law protects investors from fraudulent accounting activities. Under SOX, companies must disclose financial information so stakeholders can make informed investment decisions.
| Fun Fact The SOX Act was passed in 2022 due to scandals among large publicly traded companies. They were Enron Corporation, Tyco International plc, and WorldCom. |
SOX is critically important in ensuring financial data integrity. It has improved the quality of financial reporting and lowered the risk of fraud. Through SOX, IT organizations keep sensitive data safe from cyber attacks, such as insider threats or security breaches.
SOX’s data security framework can be summarized into the following points:
Publicly traded companies in the US need to comply with the following SOX requirements:
| Requirements | Description |
| Internal Controls | Ensuring accurate and reliable financial statements to prevent or discover problems and ensure goals are achieved |
| Auditor Independence | Prohibiting audit firms from providing non-audit services to their audit clients to prevent conflict of interest |
| Corporate Responsibility | Forcing executives to review financial reports and certify them as “fairly presented” |
SOX and the Cloud
The SOX extends to cloud computing when it involves storing and processing financial data. It requires businesses to establish controls to guarantee the accuracy and security of financial data in the cloud. Examples of this are encryption and access control.
Cloud service providers must provide features and tools that help customers fulfill their SOX compliance obligations. Audit trails and data backup solutions are examples.
Executives who purposefully submit incorrect documentation are fined up to 5 million dollars and 20 years in prison.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI DSS is a contractual commitment to secure payment card information against fraud. Businesses that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information must maintain a secure environment for compliance.
The independent body, PCI Security Standards Council, enforces PCI DSS to create comprehensive payment card security processes. They allow for proper detection, prevention, and response to security issues.
| Note PCI DSS is a standard, not a law. It is enforced through contracts between businesses that process payment card transactions and the payment brands. |
Payment security is essential for every business handling cardholder data. Here are the 12 requirements of PCI DSS:
PCI DSS and the Cloud
PCI DSS requires that cardholder data stored or processed in the cloud is securely protected. Both the cloud service provider and user must implement the following to stay compliant:
- Secure Networks
- Vulnerability Management Programs
- Access Controls
- Regular Monitoring and Testing of Networks
Fines range from $5000 to $50,000, excluding legal and settlement amounts for security breaches when merchants are not PCI DSS compliant.
More than any fine or jail sentence is the damaged reputation any company would experience for violating the above compliances. Thus, users should learn proper implementation.
GLBA (Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act)
Gramm-Leach-Billey Act or GLBA is a federal law that mandates financial institutions like banks, credit unions, insurance companies, and more to protect the sensitive financial data of every customer.
GLBA ensures that financial service providers implement safety measures against data breaches and unauthorized access. It has three key rules that organizations must follow, and these are:
- Financial Privacy Rule
The Financial Privacy Rule emphasizes transparency. It requires financial instructions to tell customers:
- what personal financial data they collect
- how they use it
- Who they share it with
Before sharing data with third parties, companies must give customers the chance to opt out. This guarantees users have some sort of control over their financial information.
- Safeguards Rule
GLBA’s Safeguard Rule makes sure that financial institutions take active steps to protect customer information. Companies must creates a written security plan that outlines how they will protect sensitive data from hackers, unauthorized access, and data leaks.
The plan should also include employee training, regular risk, assessment, and strategies to handle potential security threats.
- Pretexting Rule
The Pretexting Rule is all about preventing fraud. It prohibits anyone from getting access to personal financial information through impersonation, phishing scams, social engineering, or other deceitful means.
Financial institutions must educate their employees on how to recognize and prevent those types of attacks.
GLBA and the Cloud
Since many financial institutions rely on cloud services for data storage and processing, GLBA compliance in the cloud requires financial firms to:
- Choose cloud providers with strong encryption and security policies.
- Regularly audit cloud-based financial records for vulnerabilities.
- Limit access to customer financial data and ensure authentication measures are in place.
Non-compliance with GLBA can result in penalties of up to $100,000 per violation for institutions and $10,000 per violation for individual executives. Executives, employees, and other individuals who intentionally violate GLBA regulations may even face imprisonment for up to five years.
FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act)
The Federal Information Security Management Act is a federal law designed to strengthen the security of government data and IT systems. It applies to federal agencies, state agencies handling federal data, and private companies that contract with the US government.
FISMA’s goal is to ensure that sensitive government informatio remains secure. This law requires agencies to adopt a risk-based approach to cybersecurity—meaning they must regularly assess and update their security measures based on evolving threats.
To meet FISMA requirements, organizations must follow these core security principles:
- Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment is the foundation of FISMA compliance. Before an organization can handle sensitive government data, it must first understand the risks it faces. This includes:
- identifying potential weaknesses in its own IT infrastructure
- evaluating external threats (e.g., cyberattacks)
- considering internal risks (like insider threats)
A strong risk management strategy involves:
- Regular security audits to detect vulnerabilities before they become threats
- Classifying data based on sensitivity to ensure that the most critical information gets the highest level of protection
- Developing incident repoer plans so agencies know how to react in case of a breach
By consistently monitoring risks, organizations can stay ahead of online threats rather than reacting only after an attack occurs.
- Security Controls Implementation
FISMA requires agencies to put effective security controls in place to protect government systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. These controls cover multiple areas, ensuring a layered defense strategy that guards information at every level.
Some key controls include:
- Encryption – Scrambling sensitive data so even if it’s intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key
- Access Controls – Ensuring that only authorized personnel can access specific data or systems based on their job roles
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Requiring users to verify their identity with multiple steps (like password + fingerprint)
- Security Awareness Training – Educating employees and contractors about cybersecurity risks, phishing attacks, and proper data handling procedures
Agencies must also tailor their security controls to the nature of their operations. For example, a federal healthcare agency might prioritize electronic health record (EHR) protection, while a defense-related agency might focus on classified information security.
- Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
FISMA compliance does not end after security measures are implemented. Threats evolve constantly, so agencies must continuously monitor their systems for suspicious activity and report security incidents immediately.
Key aspects of continuous monitoring involve:
- Automated threat detection tools – these tools track system activity in real-time and flag unusual behavior
- Regular penetration testing – cybersecurity attacks simulate attacks to identify vulnerabilities before real hackers can exploit them
- Incident response and breach reporting – if an incident occurs, it is reported immediately to the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and other relevant authorities
By maintaining real-time oversight of their security posture, organizations can detect and respond yo threats faster—minimizing the possible damage of cyberattacks.
FISMA and the Cloud
With the growing reliance on cloud services, FISMA compliance extends to cloud environments. Any cloud service provider (CSP) working with a government agency must comply with FedRAMP.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program, or FEDMA, is a standardized security framework that ensures cloud providers meet federal security requirements. To achieve FISMA compliance in the cloud, organizations should:
- Use FedRAMP-certified cloud service providers.
- Encrypt sensitive data during storage and transmission.
- Conduct continuous security assessments of cloud infrastructure.
- Ensure strict access controls to prevent unauthorized data access.
Failure to comply with FISMA can result in loss of federal contracts, reputational damage, and financial penalties. Agencies that fail to meet security requirements may also face stricter oversight and additional regulatory scrutiny.
Implementing Compliance Standards
Compliance refers to structures built to ensure your business obeys the rules, regulations, and laws that govern your operations. For implementation, first, you need to identify all regulations that apply to your business. Then, establish comprehensive policies and procedures, etc.
| Reminder These requirements are meant to secure your business operations, no matter how challenging. Meeting them is a necessary step in operating and running business operations. |
Valuing compliance helps you with the following:
- Establishing business trustworthiness by enhancing reputation
- Avoiding paying hefty fines due to negligence and non-compliance
- Maintaining a clear standard on what you can and cannot do in your business
- Establishing a secure working environment for your team
- Accessing more customers since compliance is necessary to enter specific markets
Achieve these benefits by learning the best practices for implementing compliance standards, using proper instruments, and monitoring correctly.
Best Practices for Implementation
- Develop clear policies and procedures and actively educate your team about them. This practice should involve compliance requirements, cybersecurity best practices, and handling sensitive data.
- Implement robust security protection procedures such as encryption, antivirus software, a privacy policy, access control, and secure storage.
- Administer strict adherence to documentation requirements, as you want to avoid any oversight in the documentation process. This practice covers all changes, specifications, plans, procedures, and files.
- Leverage monitoring and logging mechanisms to record all business compliance activities.
- Conduct regular compliance reviews and audits to assess departmental compliance. This practice helps identify areas for improvement and determine corrective actions.
- Check on your service providers and ensure they comply with relevant standards.
- Develop an incident response plan in case of any cyberattack or security violation.
Choosing the Right Tools
Compliance management tools help IT businesses comply with requirements, policies, and standards. These tools offer risk assessments, policy and procedure management, audit trails, and reporting.
Your tools should at least do the following:
- Automate tasks and workflows.
- Handle risk management issues.
- Assure that your business policies and procedures align with applicable laws and regulatory requirements.
Your tools should be able to keep up with evolving requirements, so it is crucial to select appropriate tools for compliance management. Consider the following features before choosing:
| Criterion | Explanation |
| Policies and Procedures | Well-documented policies provide clear directives for employees, sensitive data management, and standard adherence. |
| Integration Capability | With integration capability, every team can collaborate with existing workflows and systems for better processes. |
| Usability | User-friendliness and functionality contribute to the overall user experience. |
| Scalability | Scaling with your business’ growing compliance needs is necessary, especially since regulations evolve. |
| Cost | Cost includes implementation expenses and setup, configuration, training, and data migration costs. Tools should have reasonable pricing, be cost-effective, and have good ROI. |
Some businesses turn to artificial intelligence (AI) tools to streamline processes in compliance management. AI helps improve accuracy in compliance-related tasks and reduce errors in data analysis, reporting, and monitoring.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Compliance requirements and standards change over time. New laws, updates, and interpretations are the typical factors that influence the changes in these guidelines. Thus, having a standard system that is flexible to new updates is ideal as it will let your business adjust compliance activities.
Here’s an example of a continuous improvement cycle:
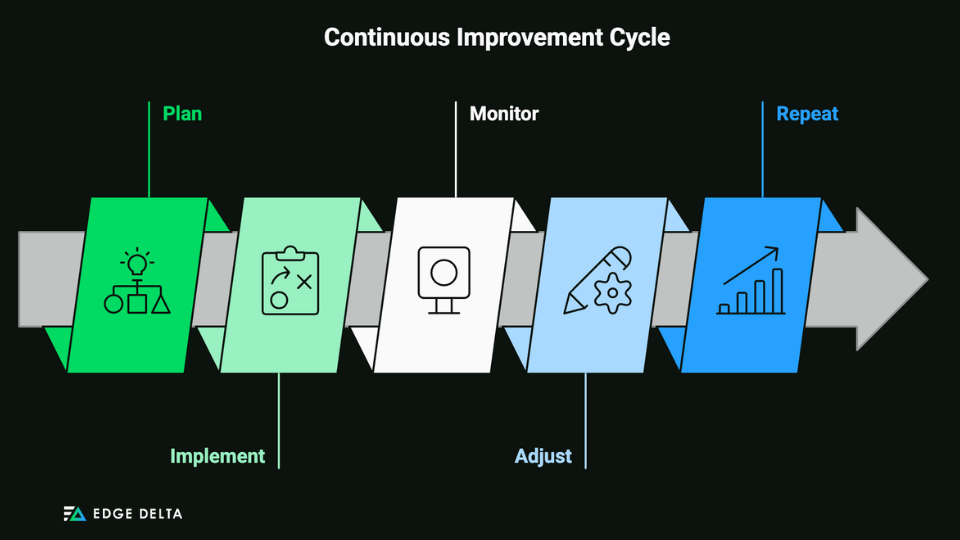
- Plan: Establish compliance processes and procedures, including your objectives and strategies.
- Implement: Put your plan into action. Utilize tools, orient your team, and integrate compliance measures.
- Monitor: Observe compliance activities and analyze performance against compliance metrics and regulatory standards.
- Adjust: Make refinements to improve compliance effectiveness: revise procedures, update training programs, or enhance controls when needed. Take this chance to address deficiencies or emerging risks.
- Repeat: Repeat the cycle and build on the insights gained from previous cycles
This process allows you to adapt to regulatory requirements and continuously improve compliance practices.
Continuous monitoring and adjustment empower you with the following capabilities:
- Spot surfacing threats.
- Align with organizational changes.
- Implement audits and assessments to ensure the effectiveness of compliance practices.
- Identify and assess non-compliance risks.
- Foster a culture of responsibility.
Staying updated on changing laws, regulations, workplace norms, and industry standards should be a norm.
Challenges in Compliance Management
IT businesses must comply with requirements and standards regardless of size to drive accountability and maintain a competitive advantage. However, regulations’ sheer volume and complexity make complying challenging and time-consuming.
You have to face gaps in employee education, siloed functions, the absence of centralization, and AI deployment concerns.
Understand the most common compliance issues and learn ways to address them below.
Common Challenges
As a compliance officer or IT business owner, you are bound to encounter some compliance headaches. Here are the challenges you must solve to avoid issues they may cause.
Alt tag: Common Challenges in Managing Compliance
Source: 7.png
Complex Regulations
Regulatory standards often cover a wide range of aspects. They can be notoriously complex because they change in response to new challenges, technologies, and societal changes.
Standards could also overlap and create a web of requirements that must be navigated simultaneously. This problem usually happens for companies that operate in multiple countries. They need to abide by local regulations, further complicating compliance efforts.
Gaps in Staff Compliance
Compliance enforcement practices and interpretations vary when unclear, adding uncertainty to your compliance efforts. This issue highlights the importance of employee education. Remember that policies hold no weight if they are not understood and followed by everyone.
Siloed Functions
Often, compliance processes are made in response to specific events like new regulations, litigation, and criminal investigations. When organizational departments operate in silos, compliance efforts are only reactive rather than holistic.
Lack of Centralization
Spreadsheets and shared files are standard tools for compliance management. However, manual usage without centralization makes tracking and finding important compliance documents hard.
Outdated tools are also not designed to keep up with frequent updates and constantly changing regulations. For instance, manually updating each spreadsheet in multiple locations can be tedious. Rekeying or copy-and-pasting also introduces human error.
Different systems also store compliance data in disparate formats and locations. This data fragmentation makes it challenging to consolidate and analyze data.
AI System Flaws
Despite its benefits, AI poses significant risks in compliance management. An example of compliance risk in AI is that these systems may not understand how decisions are made. The value of massive records that AI systems store can make them attractive targets for cyber-attacks.
Overcoming Challenges
Despite the inevitability of compliance challenges, dedicated teams should know there are always ways to get around them. Established companies should consider the following practices to keep up their growth pace and for start-ups to prepare.
Training your team
Conduct regular training and updates to ensure your staff understands the reasons behind your compliance efforts, especially the changes you implement. You also need them to know their roles and responsibilities within your compliance framework.
| Pro Tip Consider a reward system for staff who embrace regulatory compliance changes. This practice will help employees understand the importance of staying compliant and be motivated to continue doing so. |
| <table border=”1″ cellpadding=”10″><tbody><tr><td><p><strong>Pro Tip</strong></p><br /><p><span style=”font-weight: 400;”>Consider a reward system for staff who embrace regulatory compliance changes. This practice will help employees understand the importance of staying compliant and be motivated to continue doing so. </span></p></td></tr></tbody></table> |
Overcoming the silo mentality
Establish clear communication channels within departments to encourage collaboration. This step ensures that departments respond to regulation changes considering the broader compliance framework.
Employing a technology solution for a centralized system
A centralized compliance management system promotes consistency and efficiency. It reduces redundancy by streamlining compliance processes. With this strategy, you can use a particular software to automate tasks, notifications, and approvals.
Your system should provide a centralized view of compliance activities, such as compliance status, issues, and trends across your business. This centralization speeds up and simplifies monitoring, reporting, and risk mitigation.
Hiring dedicated experts
Focus on other parts of your business by leaving your compliance paperwork and concerns to a compliance manager or consultant. These experts take responsibility for monitoring, reviewing, and creating your business’ compliance program. With this system, you can demonstrate your business’ understanding and diligence in following your legal responsibilities.
Conclusion
Among the critical requirements of compliance in IT are GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI DSS. Compliance is effective when you learn the best practices, choose the right tools, and continuously monitor.
The ever-evolving nature of regulations makes compliance a challenge. Nevertheless, businesses must be in good standing with regulators. This way, they can avoid legal liabilities, show ethical responsibility, and enhance trust with clients, partners, and the public.
FAQs on Compliance Requirements and Standards
What is the most important aspect of compliance?
Effective compliance requires continuous monitoring. With this process, IT firms can quickly detect and address risks before they affect operations. Regular audits are also crucial as they establish security and privacy protocols.
What are the three areas of compliance?
Compliance regulations cover IT firms’ technical, administrative, and physical security and data protection areas. These three aspects cover all IT operations and protect all sensitive data.
What is the ISO standard for compliance programs?
ISO 37301 is the standard for compliance programs. It provides a framework for all organizations to manage compliance risks and ensures that every firm operates legally, ethically, and socially.
Sources: