The change in IT infrastructure has been huge, from systems like Lotus Notes of the ’90s to the current multi-cloud complex environments. This development indicates the solution to growing scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness needs.
Adopting a multi-cloud strategy has been a critical enabler in reaping benefits from many cloud computing and storage services. Multi-cloud servers will yield benefits, such as escaping from the lock-in of one provider and increased system resilience, with the potential for cost reduction.
Want Faster, Safer, More Actionable Root Cause Analysis?
With Edge Delta’s out-of-the-box AI agent for SRE, teams get clearer context on the alerts that matter and more confidence in the overall health and performance of their apps.
Learn MoreIn this article, understand what multi-cloud observability is, discover how to implement multi-cloud observability and its importance.
Key Takeaways:
- Multi-cloud observability enables real-time analysis of applications and infrastructure across various cloud platforms to enhance business agility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
- Implementing multi-cloud observability is crucial for optimizing performance to ensure security and manage costs in complex cloud environments.
- Challenges like architectural complexity and security concerns in multi-cloud observability can be addressed through strategic planning and adopting best practices.
- Selecting the right multi-cloud observability tools, such as Edge Delta, Datadog, or Splunk, is key to efficiently managing and analyzing diverse cloud operations.
- Multi-cloud observability is essential for modern IT infrastructure, offering strategic advantages in a cloud-centric world through effective implementation and tool usage.
What Does Multi-Cloud Observability Mean?
Multi-cloud observability is the ability to simultaneously analyze and understand the performance or condition of applications and the whole infrastructure across multiple cloud environments.
Multi-cloud or hybrid cloud architecture involves mixing various cloud services from providers. Businesses that use Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to design a flexible and resilient IT infrastructure are the most avid users of this approach. Multi-cloud environments use different vendors’ best technologies and services to provide users unparalleled stability compared to single-vendor models.
Business models for agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness are the drivers for creating multi-cloud strategies. Companies can customize their infrastructure through these strategies according to their specific needs.
With an understanding of the concept and benefits of multi-cloud observability, let’s explore why it’s becoming an indispensable strategy in modern.
Note:
In multi-cloud observability, the challenge lies in monitoring individual cloud environments and aggregating and correlating data from different cloud providers. Effective multi-cloud observability strategies often leverage advanced analytics, machine learning, and automation to streamline data collection, analysis, and visualization processes across disparate cloud environments.
Why Implement Multi-Cloud Observability? The Benefits
Implementing multi-cloud observability is crucial for businesses leveraging cloud services from multiple providers. The technology helps to gain insights needed to manage complex environments efficiently, ensuring optimal performance, security, and cost management.
Here are the reasons why it is essential to implement multi-cloud observability:
- Flexibility and resiliency, which provide a better business continuance ability due to the distribution of the resources among several cloud platforms
- Performance Optimization: Helps to locate and solve problems between different clouds within a very short period.
- Real-time Insights: Help respond promptly to any anomaly or threat.
- Cost Management: Helps to identify and correct potential problems with inefficient use of cloud resources.
Proper implementation of multi-cloud observability will be vital in ensuring the full realization of multi-cloud architecture and addressing its inherent observability challenges.
Challenges in Multi-Cloud Observability
Navigating multi-cloud observability comes with unique challenges that users must address to harness its full potential. By overcoming these hurdles, organizations can unlock the full benefits of multi-cloud observability and ensure resilience systems.
The following are some of the challenges faced by multi-cloud observability:
1. Architectural Complexity
The complexity of integrating various platforms and technologies into multi-cloud environments is one of the challenges faced by multi-cloud observability. This complexity can raise the risk of inefficiencies and complicate operational flow.
- Disaster Recovery and Cloud Sprawl: Disaster recovery planning becomes infinitely more challenging in multi-cloud observability because you must consider each cloud provider’s failure mode. Cloud sprawl is also a consent as it could lead to inefficient resource use.
2. Security Across Cloud Platforms
Maintaining a security posture consistently across all the cloud platforms can also be another challenge. Because every provider will have security protocols to ensure a secure multi-cloud environment, it can be difficult to implement another security measure.
Understanding these challenges is important so you can tailor your implementation of multi-cloud observability according to your needs.
How to Implement Multi-Cloud Observability: A Step-by-step Guide
Implementing multi-cloud observability is an operational best practice representing the setup of systems and practices allowing you to monitor and study applications and infrastructure across your organization on multiple cloud-based platforms.
Here are simplified explanations of how to implement Multi-cloud Observability:
Planning and Strategy
First, you must define the objectives you want to achieve with multi-cloud observability. These objectives can range from straightforward goals, like ensuring high availability and optimal performance, to more complex ones, such as cost optimization or enforcing a consistent level of security across all your cloud environments.
Here are the crucial steps for planning and strategizing your implementation:
- Determine the relevant metrics that are most important to your service level objectives. For instance, key metrics include latency, error rates, and throughput if you focus on optimizing performance.
- Access the current configuration of your cloud environments, which includes information on running services, generated data, and how these elements interact across different cloud platforms.
- Catalog your cloud assets across different providers to fully understand what needs to be observed.
- Identify how various cloud services and applications communicate and depend on each other, pinpointing specific areas critical for observability.
Implementation Steps
Ensuring consistent collection of metrics, logs, and traces across all your cloud environments is vital, as is choosing tools for data collection that are compatible across all your cloud providers.
Follow these implementation steps:
- Incorporate service features or deploy agents that can gather detailed information about the health and performance of your applications and infrastructure.
- Standardize and normalize data from different sources to facilitate effective aggregation and analysis.
- Use a tool or platform to aggregate and correlate data from all sources, providing a unified view of your multi-cloud environment.
- Implement a centralized observability platform that can ingest, aggregate, and display data from all your cloud environments, enhancing the ease of data interpretation and decision-making.
- Apply analytical tools to aggregate data in a way that provides actionable insights. Users should use data visualization to make this information easily accessible and understandable to various stakeholders.
- Utilize tools capable of real-time data processing to identify and alert on issues as they arise quickly.
- Develop strategies for managing historical data and using it to identify trends and patterns, which can aid in predictive insights and long-term planning.
Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Observability Implementation
Develop a culture where observability becomes part and parcel of day-to-day operations, not as a reaction to incidents. Here are tips on how to do that:
- Foster a culture where observability is integral to day-to-day operations rather than just a reaction to incidents.
- Set up proactive alerts based on preset thresholds to inform your team about potential issues well in advance.
- Review your observability data and processes to ensure they align with your objectives.
- Promote knowledge sharing across teams based on observability data to support a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
- Integrate observability into your CI/CD pipeline so that monitoring and performance analysis start automatically with each new deployment.
By thoroughly addressing these aspects, organizations can establish a robust framework for implementing multi-cloud observability to monitor and manage their diverse cloud environments effectively.
Equipped with strategies to overcome these challenges, selecting the right tools is the next critical step in enhancing multi-cloud observability.
Tools for Multi-Cloud Observability
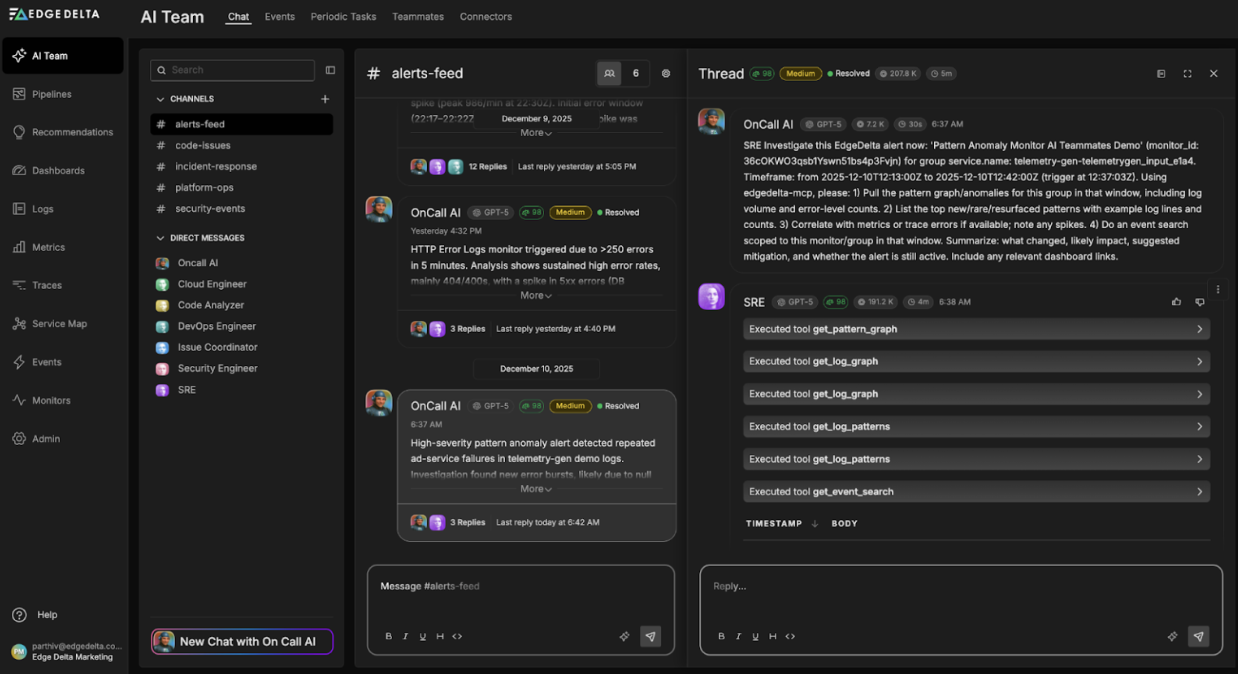
Multi-cloud observability tools help organizations handle complex cloud setups efficiently. They make managing operations easier, ensuring security and controlling costs across different cloud platforms. For example, Edge Delta is a tool that provides such multi-cloud observability, allowing companies to monitor and analyze their cloud infrastructure seamlessly:
Criteria for Tool Selection
Not all tools are made equal. To help find the best fit for your needs, consider the following factors:
- Strong Integration: Look for tools with deeper integrations into most cloud providers and their respective services to get a strong level of observability in your multi-cloud environment.
- Scale: Choose a tool that can be scalable in line with the growth of your cloud infrastructure, meaning it can handle an increased volume and complexity of data without hurting performance.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: These tools come with user-friendly interfaces, and they should be straightforward for IT personnel, developers, and decision-makers.
- Customization and Flexibility: Consider the tools you can customize at the desired level of detail in monitoring and, further, with flexibility in setting alerts, dashboards, and reports.
- Advanced Analytics: Choose advanced analytics tools that allow you to get insights from the massive amounts of collected information.
- Cost-Effective: Look for the total cost of ownership, including licensing, training, and maintenance. It should give back value for the price.
Note:
To ensure effective multi-cloud observability, adopting a unified monitoring platform capable of integrating with APIs from different cloud providers is crucial, enabling standardized metrics and logs collection for centralized analysis and cross-cloud data correlation.
Leading Tools in the Market
- Datadog: Datadog is the top multi-cloud observability application offering. It is known for its solid analytics and integration flexibility, as well as features that include more than one cloud platform monitoring.
- Splunk: With its strong capacity for data processing and visualization, it may be viewed in terms of implementing complex analytics by the organization, making it a perfect tool for multi-cloud observability.
- New Relic: Treated with applause for one of the most united observability suites and ease of use, it makes monitoring and analysis very easy for roles across organizations.
- Edge Delta: The youngest on the list, Edge Delta places its unique twist on data analysis with an edge computing approach. In this way, it processes data at the edge (wherever data is created), reducing the latency of processing the data. This way, you can gain real-time insights; this is an innovation towards multi-cloud observability.
The organization can identify the best multi-cloud observability toolset to suit their needs by choosing the right tools. They can use these tools to advance their competence in monitoring and managing the cloud environment.
Wrapping Up
Multi-cloud observability is an integral part of the modern IT infrastructure that helps businesses reap the maximum benefits from multi-cloud strategies.
Effective implementation of multi-cloud observability calls for strategic means in tools and practices that may enable these organizations to thrive in such complex environments. From there, with multi-cloud observability at play, the future of IT infrastructure management will be shaped in an ever more cloud-centric world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is multi-cloud observability, and why is it important?
Multi-cloud observability is the practice of monitoring, analyzing, and gaining insights into the performance of applications across various cloud environments. Due to the increasing adoption of multi-cloud strategies, offering organizations flexibility, resilience, and cost optimization is essential. Managing performance and identifying issues across disparate cloud platforms becomes challenging without comprehensive observability tools.
What are the key components of a multi-cloud observability solution?
A multi-cloud observability solution typically consists of monitoring, analytics, visualization, alerting, and integration components. These components work together to collect and analyze data from diverse cloud services, provide insights through visualizations, alert stakeholders about critical issues, and integrate with existing tools and processes for efficient management and resolution.