Unstructured data acquires the biggest volume, accounting for 80% of all the generated data. This data type consists of the files and content we use daily. These files include documents, videos, and sensor data.
While data is a valuable asset in the digital era, 95% of businesses think unstructured data poses a significant problem. The volume of this data type implies that businesses must innovate solutions for data storage, data privacy, and data management.
Want Faster, Safer, More Actionable Root Cause Analysis?
With Edge Delta’s out-of-the-box AI agent for SRE, teams get clearer context on the alerts that matter and more confidence in the overall health and performance of their apps.
Learn MoreKeep reading as we dive deep into why unstructured data is important and how it can help businesses grow. This article will also discuss the facts and figures, including the other two data types.
Editor’s Choice
- Unstructured data holds the biggest data volume, up to 80%.
- Structured data is part of the minority, yet it receives the majority of investments, accounting for 60% of total expenditure.
- In this digital era, data is a valuable asset for analytics, which benefits businesses.
- Semi-structured data, such as log events, is a hybrid data type, acting as a bridge between structured and unstructured data.
- Marketers must determine the compatibility of their business’ nature and the data type.
- With AI tools, 44% of businesses utilize unstructured data in their systems and processes.
- Software tools allow structured data to be extracted from unstructured data.
- 95% of businesses acknowledged the risk of unstructured data management.
How Much of Big Data Is Unstructured?
Unstructured data is the information engaged with daily. This data comes in many forms, growing 4x faster than the two data types—structured and semi-structured.
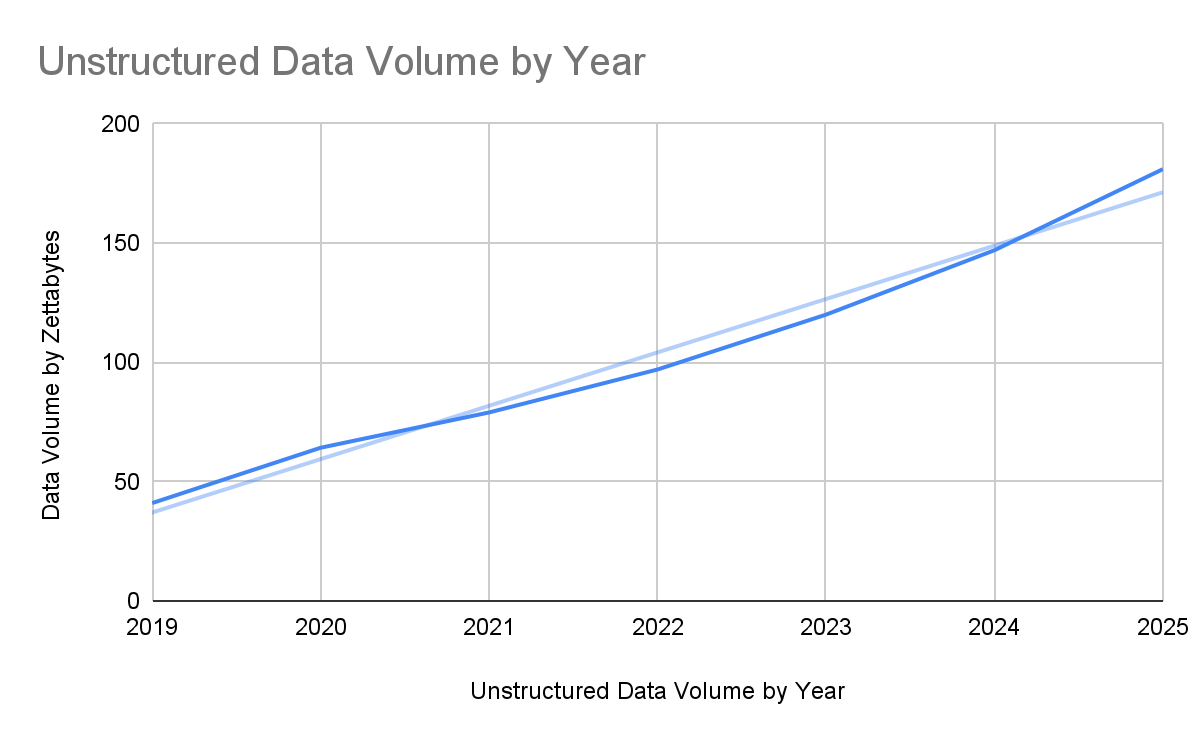
A study predicts that data will experience 181.93% growth from 2020 to 2025, and based on volume, 80% of the data is unstructured. These data can be any of the following:
- Text files: word files, spreadsheets, presentations, logs
- E-mails: the body of the message
- Data from social media platforms, such as:
- YouTube
- Mobile data: messages, location, chats
- Pictures
- Videos
- Audio
- Weather data
- Satellite images
- Sensor data
In addition, information under unstructured data can be referred to as content. The content does not follow a predefined schema or data model, making it more challenging to analyze data.
The following section will cover the three data types, their differences, and how they are relevant to business expansion.
Structured Data Vs. Semi-Structured Data Vs. Unstructured Data
Data is a collection of facts and numbers, wherein all the generated data are sourced and scaled in three different types: Structured, Semi-Structured, and Unstructured.
The data under any of these data types are the backbone of data analysis—a valuable method for business operations. It helps businesses improve their processes efficiently and effectively, boosting their productivity.
Aside from the process and operations, it can boost sales by helping marketers to understand their consumers. Marketers should know what data type is compatible with their businesses to maximize the data’s full potential.
Here, you can view the differences between the three data types:
| Properties | Structured Data | Semi-Structured Data | Unstructured Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Based on a relational database table | Based on Extensive Markup Language (XML) and Resource Description Framework (RDF) | Based on character and binary data |
| Transaction Management | Various concurrency techniques | Adapted from a Database Management System (DBMS) | No transaction management and no concurrency |
| Version Management | Versioning over tuples, rows, tables | Versioning over tuples or graphs is possible | Versioned as a whole |
| Flexibility | Schema dependent and less flexible | More flexible than structured data but less flexible than unstructured data | Not schema dependent and more flexible |
| Scalability | Very difficult to scale database schema | Scaling is simpler than structured data | More scalable |
| Query Performance | Allow complex joining | Queries over anonymous nodes | Only textual queries |
Continue reading as we further discuss the differences between the three digital data types in terms of volume and data sample.
1. Structured Data: Occupies 20% of the Total Data Generated
(boxBLOGS, Google Search Central, Almanac)
Structured data refers to organized and pre-defined data, accounting for 20% of the total generated data. This data type is easier for humans and machines to read, search, and analyze.
With its defined schema, organizations spend more on structured data, allocating 60% of the total expenditure. One of the major investors of structured data is Google.
Google Invests More in Structured Data
Google uses structured data to make the search results more engaging to users. They started investing heavily in COVID-related structured data, and then, in 2022, Google shared how they complement machine learning to structured data.
Side Note:
Structured data can be extracted from unstructured data. Business intelligence (BI) tools extract the data with the aid of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
Adding structured data to web pages keeps engagement high. Here are some of the websites that implemented structured data for their site:
- Rotten Tomatoes: Adding structured data to 100,000 unique pages resulted in a 25% increase in the click-through rate.
- The Food Network: 80% of their pages are converted, resulting in a 35% increase in visits.
- Rakuten: The search features have a 3.6x higher interaction rate on accelerated mobile pages (AMP).
- Nestle: The site experienced an 82% higher click-through rate.
SEO With Structured Data Boosts Site Discoverability and Engagement Activity
Aside from the four abovementioned websites, more sites or businesses recognize the value of structured data. Using this data type paired with SEO strategy increased mobile click-through rate in businesses—from 37% in 2022 to 43% in 2024.
The CTR on results enhanced by structured data accounts for 58% while 41% of clicks are for unstructured data results. It is worth noting that proper utilization of SEO and structured data boosts business operations and sales.
Some disadvantages must be considered when planning to use structured data. Here are the pros and cons of structured data:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to analyze for humans and machines | Limited flexibility |
| Use the same format across all systems | Requires manual data entry |
| Efficient data processing | Costly to set up and maintain |
| Easily integrated into other systems like databases and applications | Possible incomplete data if not regularly updated |
2. Semi-Structured Data: Approximately 5% to 10% of the Data Generated
(Airbyte, Geeks for Geeks)
Semi-structured data belongs to the minority, with only 5% to 10% of the total data generated. This data type cannot be organized and doesn’t follow a schema yet has structural properties.
The structured properties make it easier for the data to analyze. Data contains metadata and tags that provide additional information. This information includes author, data, or keywords, which can be used to identify specific characteristics.
Metadata Definition
Metadata is data that describes other data, excluding the content of the data itself. Examples of basic metadata are as follows:
- Author
- Date Created
- Date Modified
- Tags
- File Size
In observability, engineers use semi-structured data in the form of log events. Log events are timestamped records generated by software, capturing information about system behavior. They provide insights into application performance, errors, and user interactions. Analyzing log events helps identify issues, troubleshoot problems, and optimize system performance, enhancing overall system observability.
Sample data with additional information is a photo taken on a smartphone. The image will have attributes like date and time stamp, geotag, and device ID. Other examples are JSON and XML files, which embed URLs, meta tags, and domains.
With these attributes, more organizations use semi-structured data for analysis and management. However, semi-structured data poses some disadvantages.
The table below shows the pros and cons of semi-structured data:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Flexible in terms of data storage and management | Sometimes difficult for data storage because of its lack of fixed and rigid schema |
| Scalable and well-suited for managing large volumes of data | Complex to manage and process |
| Faster data processing | Often lacks standardization and consistency |
| Easily integrated with other types of data | Processing the data can be more resource-intensive |
| Contains more contextual information, such as metadata or tags | Challenging to find the right tools and technologies for a particular use case |
| Portable data | More difficult to secure compared to structured data |
3. Unstructured Data: Majority of Data volume of Up to 80%
(Fivetran, Geeks for Geeks, boxBLOGS )
Unstructured data does not conform to a pre-defined schema. This data is unorganized and difficult to analyze, yet it yields the biggest data volume of up to 80%.
Computer programs cannot easily use data, but they provide a comprehensive data story. However, the lack of structure makes the companies invest less in this data type.
With the current AI trend, unstructured data keeps growing at an astounding annual growth rate of 55% to 65%. Data processing and extraction have changed and have become easier with the proliferation of AI and ML algorithms.
Did You Know?
The average employee uses 37 tools for work at most. Seventy percent of the tools are used for unstructured data.
The emergence of AI paved the way for big data to reveal its importance and full potential. Despite the inherent value, only 44% of organizations are willing to invest in unstructured data.
According to International Data Corporation, there is an inverse ratio of IT investment between structured and unstructured data. Even though 80% of data is unstructured, 40% is allocated, while 60% is spent on structured.
The table below shows the pros and cons of unstructured data:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Flexible due to lack of schema | Difficult to store and manage |
| Portable and scalable data | Complex and error-prone data indexing |
| Use a variety of business intelligence and analytics applications | Security issues |
Final Thoughts
Data is one of the most valuable assets, especially in the business. The unstructured data volume continues to grow, which plays a crucial role in shaping the digital and data-driven era.
While it’s true that they are difficult to analyze, this data type offers profound insights for better decision-making. The massive data influx resulted in the tandem of AI, wherein most of the unstructured data can be AI-processed.
Frequently Asked Questions on Unstructured Data
How much of our data is unstructured?
Unstructured data holds the biggest volume, accounting for 80% of the data generated.
What percentage of data is structured and unstructured?
Structured data is approximately 20%, while unstructured data accounts for 80%. Sometimes, it can go up to 90%.
Is 90% of data unstructured?
Yes, unstructured data can go up to 90%, with a minimum rate of 80%.