Single Pane of Glass (SPoG) is a term which refers to a dashboard or platform that can display data from a variety of sources in one single, centralized view. They are critical for organizations working to develop a comprehensive, unified truth, especially those with a multitude of moving parts. By providing a unified view, SPoG facilitates optimized performance tracking and problem diagnosis, along with enabling informed decision-making to improve operational efficiency.
This article will explore SPoG as it relates to the observability space, acting as the “Complete Guide to Single Pane of Glass in Observability”. It will cover common SPoG use-cases, benefits, challenges, and more, to help you understand the importance of a unified view for achieving functional Observability.
Want Faster, Safer, More Actionable Root Cause Analysis?
With Edge Delta’s out-of-the-box AI agent for SRE, teams get clearer context on the alerts that matter and more confidence in the overall health and performance of their apps.
Learn MoreKey Takeaways
- With SPoG, IT managers can get enhanced visibility, efficiency, productivity, and collaboration.
- Implementing SPoG presents various challenges, in particular with respect to data integration, and scalability.
- Understanding appropriate strategies can help overcome SPoG roadblocks.
- With the best practices in place, SPoG simplifies management and monitoring functionalities by combining data from several sources into a single view.
What is a Single Pane Of Glass in Observability?
In observability, a Single Pane of Glass offers a straightforward approach to gauging a system’s internal conditions using its generated log, metric, and trace data. With this process, teams can maintain system security, performance, and reliability.
The following section briefly discusses the key benefits associated with an effective SPoG platform.
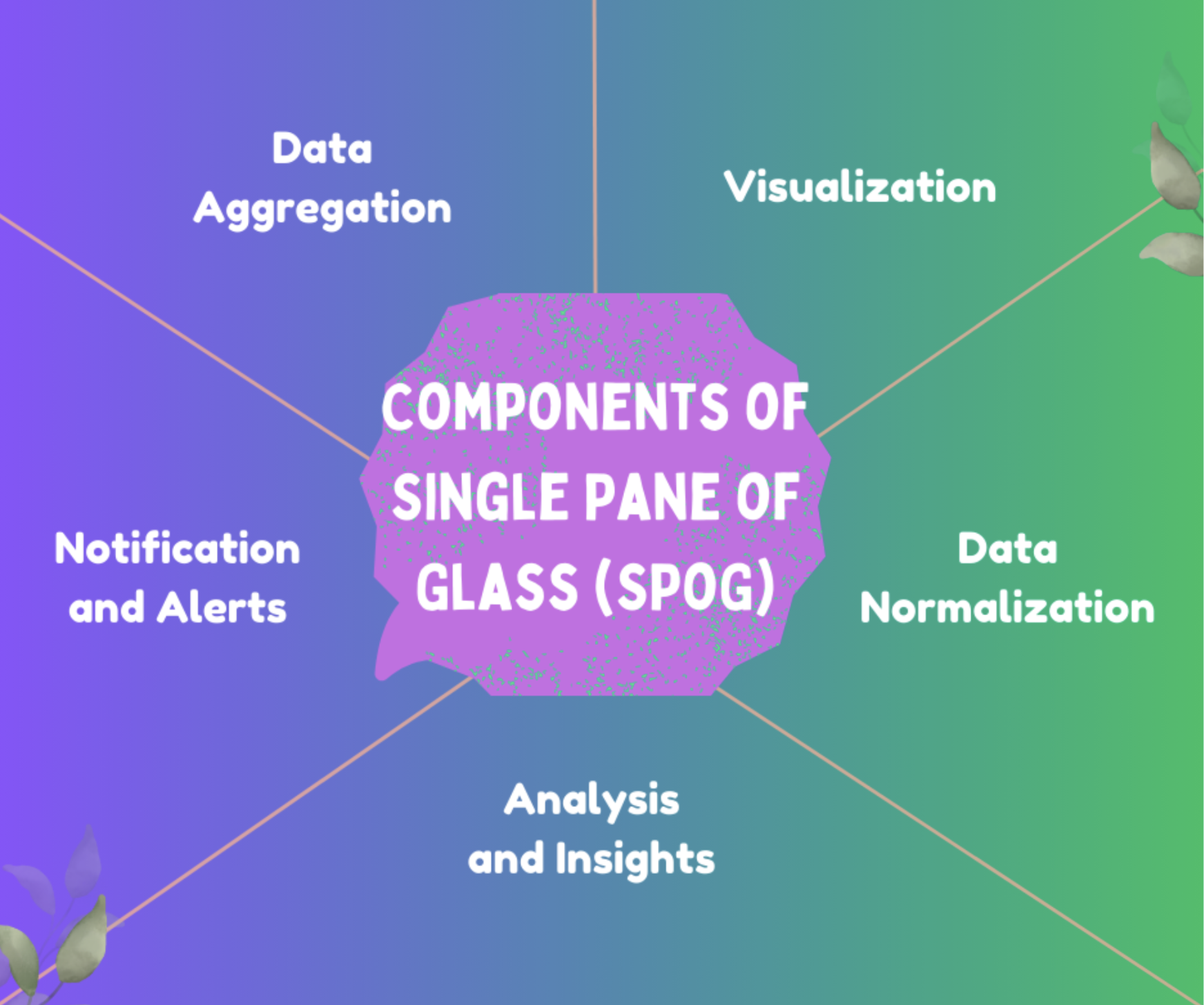
Collection and Aggregation
SPoG’s initial function is gathering and aggregating telemetry data from infrastructure components like servers, networks, software, and security systems. It consolidates the data into a single, solitary repository to facilitate access and analysis.
Transformation
Since data from several components are in different formats, SPoG transforms them for consistency. This process improves data integrity and usability by ensuring that data from diverse sources can be compared and analyzed consistently.
Visualization
With consistent data, SPoG provides graphical representations to offer a comprehensive view. This process includes providing data insights that are easily understandable and actionable by displaying information in charts, graphs, and dashboards.
Analysis and Insights
SPoG also produces reports and insights by analyzing the gathered data. With this function, teams can conduct comprehensive analyses for automated reporting to assist in making strategic decisions and enhancing operational efficiency.
Notifications and Alerts
SPoG provides notifications and alerts by monitoring data to identify irregularities or problems. When incidents happen, the dashboard sends alerts to relevant personnel. This feature allows proactive incident response to reduce downtime and improve user experience.
Benefits of SPoG
Managing massive data volumes from various sources is challenging. With SPoG, teams can implement observability practices like performance monitoring, issue detection, and informed decision-making.
These features provide several benefits to users, such as the following:
Enhanced Visibility
SPoG consolidates system data into a single interface, providing comprehensive system visibility. As a result, IT personnel can quickly monitor system activity, track performance, and spot issues early.
Efficiency and Productivity
By reducing the need to switch between several tools, SPoG streamlines operations for higher productivity. It also lowers downtime by speeding up issue detection and resolution. As a result, it improves resource allocation and prioritization based on real-time information.
Improved Collaboration
SPoG promotes cross-functional collaboration by offering shared visibility to system data. By encouraging communication and knowledge exchange, this shared interface helps teams collaborate more successfully to identify problems, maximize performance, and implement improvements, driving better organizational outcomes.
Challenges with Implementing SPoG
Incorporating organizational data into a Single Pane of Glass (SPoG) is challenging but valuable work. With careful preparation and planning, teams can effectively handle these hurdles and ensure successful deployment.
Below is a list of common challenges associated with implementing an single pane of glass solution.
Data Integration
Problem: Data from several sources normally arrives in different formats, and as such integrating them takes time and effort.
Recommended solution: Make use of standardized data formats and robust integration tools to ensure formatting consistency.
Scalability
Problem: Integrating new data sources into a system can cause drops in performance and usability. Thus, scaling can be problematic.
Recommended solution: Consider scalability when designing the system and use cloud-based solutions.
Security and Privacy
Problem: Since SPoG consolidates all data, it may even include sensitive information in its aggregation.
Recommended Solution: Put role-based access control (RBAC) and other robust security policies into practice.
Use Cases and Examples of SPoG
SPoG provides a unified view of systems and infrastructure which aids in the completion of several different types of processes and tasks. For instance, the comprehensive view can offer key insights necessary to improve performance throughout business units by monitoring IoT devices and acting as a common information point for partners, suppliers, and customers.
Below is a description of common use cases and examples of SPoG:
Use Case: IT Infrastructure Management and Monitoring
Example: Centralizes server, network, and application monitoring to swiftly detect problems.
Use Case: Performance Ability and User Experience
Example: Aids IT and DevOps teams in improving performance and end-user satisfaction.
Use Case: Cybersecurity
Example: Incorporates security tools to offer a unified view of vulnerabilities and threats.
Use Case: Application Performance Management
Example: Aggregates performance metrics to maximize the efficiency of the application and user experience.
Use Case: Cloud Management
Example: Consolidates cloud resources across several platforms to improve cost and control.
Use Case: Business Analytics
Example: Combines data from various business tools to provide insights and aid in the decision-making process.
Use Case: Customer Support and Service Management
Example: Integrates CRM and service desk tools to enhance customer support and service management.
Best Practices for Implementing SPoG
By adhering to the following best practices, organizations can adopt a single-pane-of-glass solution to boost observability, increase decision-making, and support overall company goals.
Clear Goal Definition and Requirements Gathering
Clearly define the goals you aim to accomplish with SPoG. This way, you can determine precise objectives to direct the implementation process. These goals include increasing system observability, optimizing performance monitoring, or simplifying IT operations.
Selection of Appropriate Tools and Technologies
Choose platforms and solutions that satisfy your unique requirements and work well with the systems you already have in place. Ensure the tools have robust analytics, visualization, and data integration capabilities.
Emphasis on Data Quality and Consistency
Ensure that the data included in your SPoG is accurate, dependable, and current. Implement procedures for data validation and cleansing to maintain high-quality data.
Regular Maintenance and Updates
Monitor your SPoG solution’s performance and make necessary adjustments to ensure that it can efficiently manage massive data volumes. Update and improve the system frequently to guarantee peak performance.
Conclusion
Implementing Single Pane of Glass (SPoG) in observability is a transformative technique for modern businesses. By consolidating data from multiple sources into a single interface, SPoG improves team cooperation, efficiency, and visibility.
While it has its fair share of challenges, the advantages of more efficient operations, better decision-making, and streamlined processes make the investment extremely valuable. By utilizing SPoG, organizations may track system performance more effectively, find and fix problems quickly, and produce better business results.
FAQs on Single Pane of Glass Observability
What is a Single Pane of Glass model?
The ‘Single Pane of Glass’ model refers to the unified view of an entire enterprise’s system. With this interface, teams can establish one comprehensive data source within an organization. Generally these models display data from several sources into one dashboard.
What are the benefits of a Single Pane of Glass?
Due to its comprehensive view, single Pane of Glass functionality facilitates better group coordination and teamwork. A single data source reduces confusion and friction and allows for consistent analysis.